IR1101-K9 Rugged Series Router with two LTE modules (LTE and LTE-Advanced with carrier aggregation)
468.47$
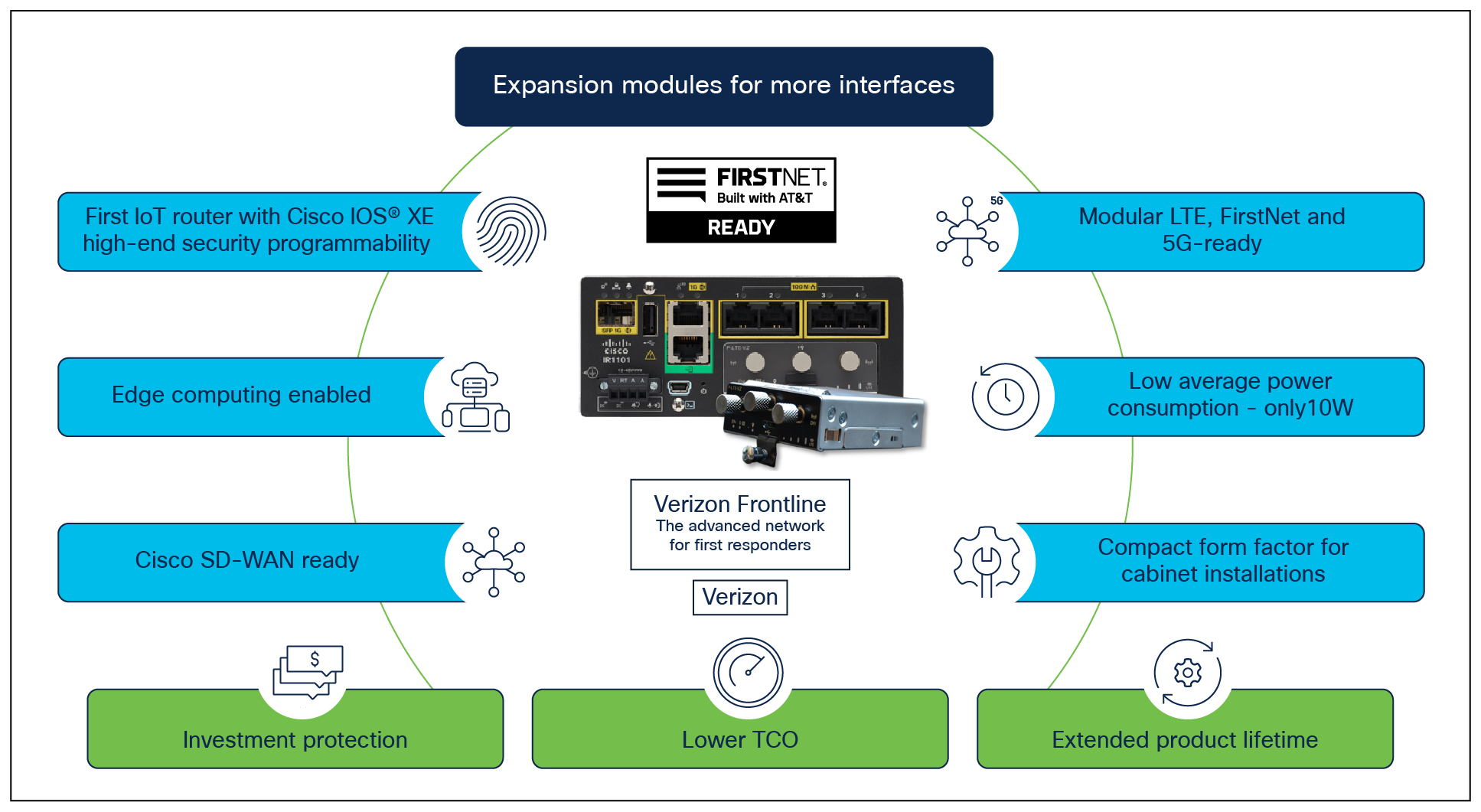
Product highlights |
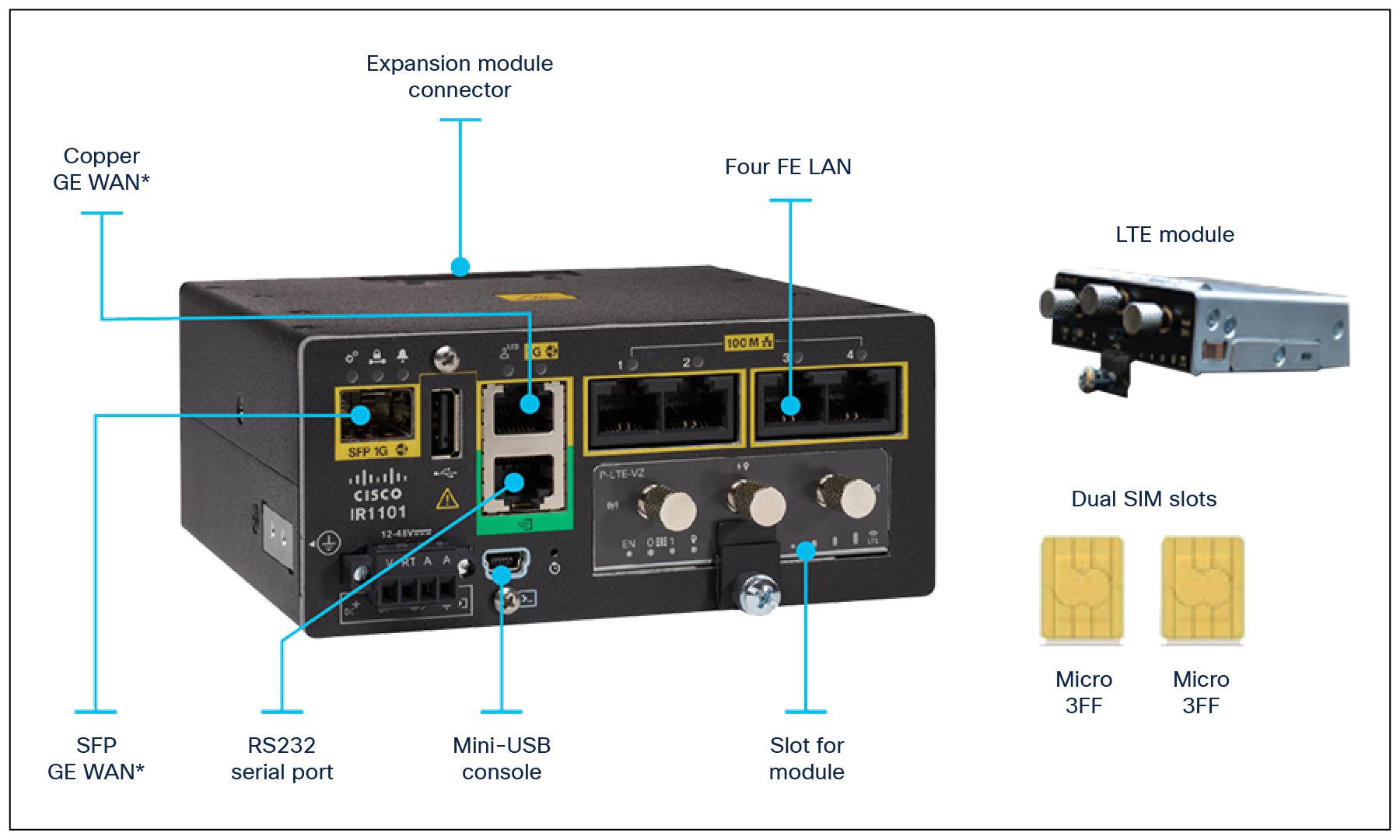
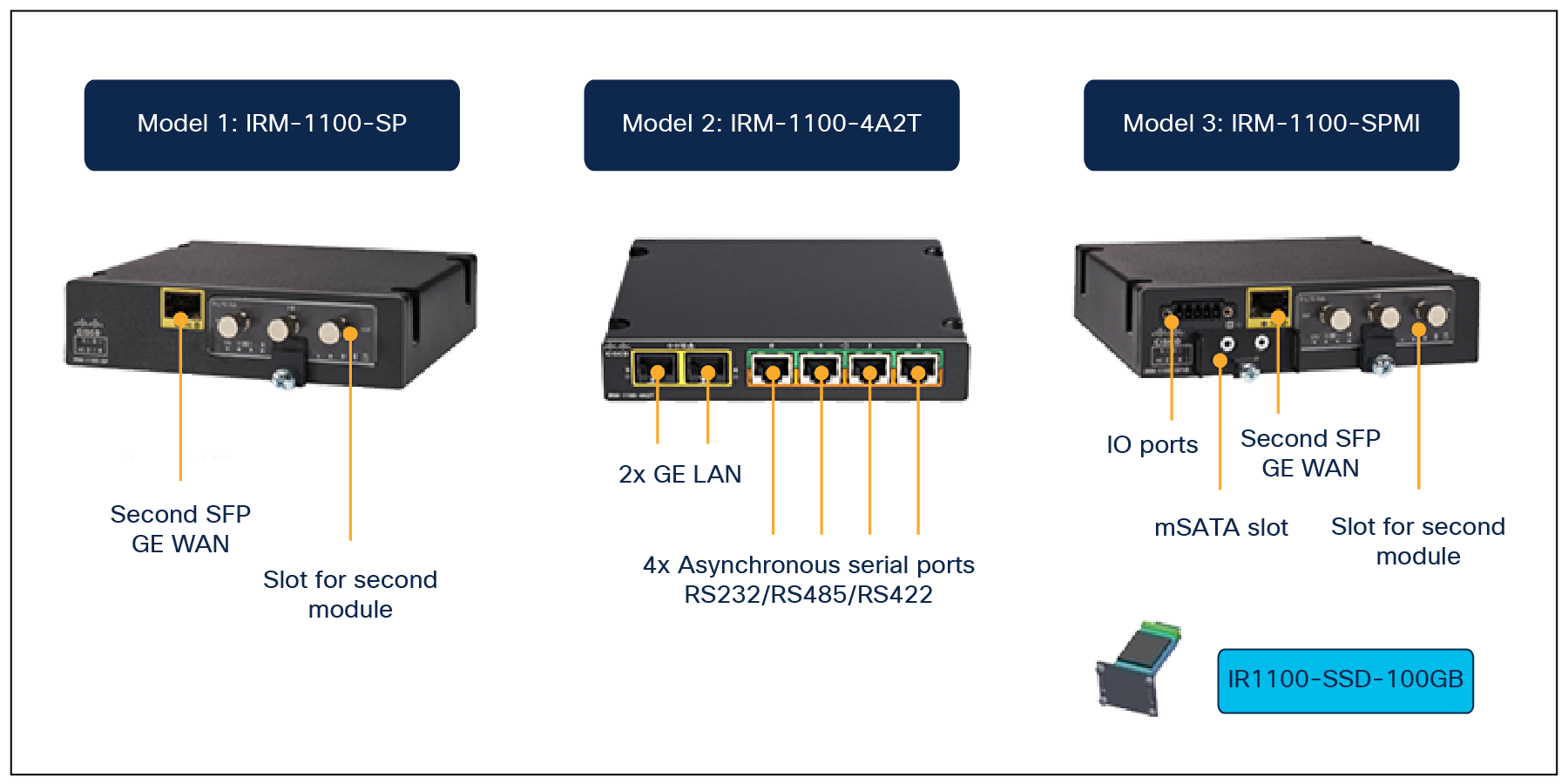
Figures 1, 2, and 3 offer visual views of product components and expansion modules.
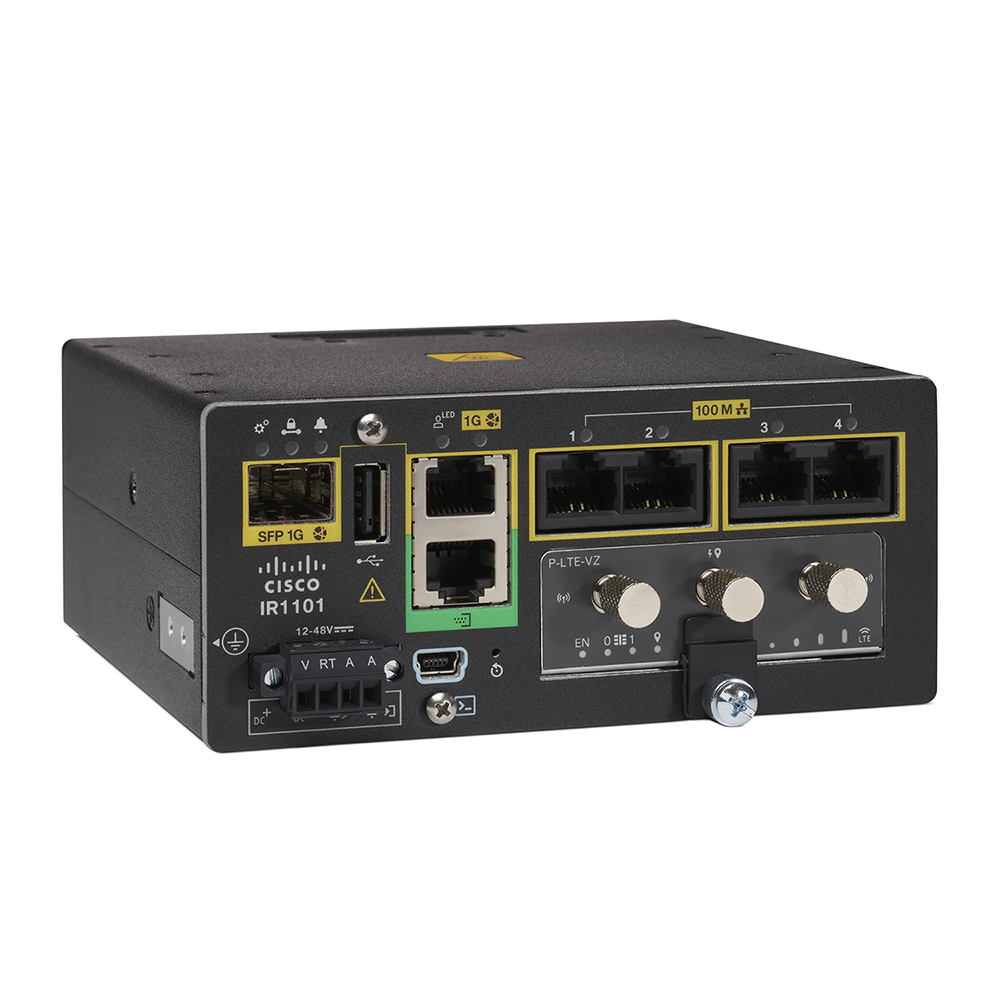
Cisco IR1101 base platform front view
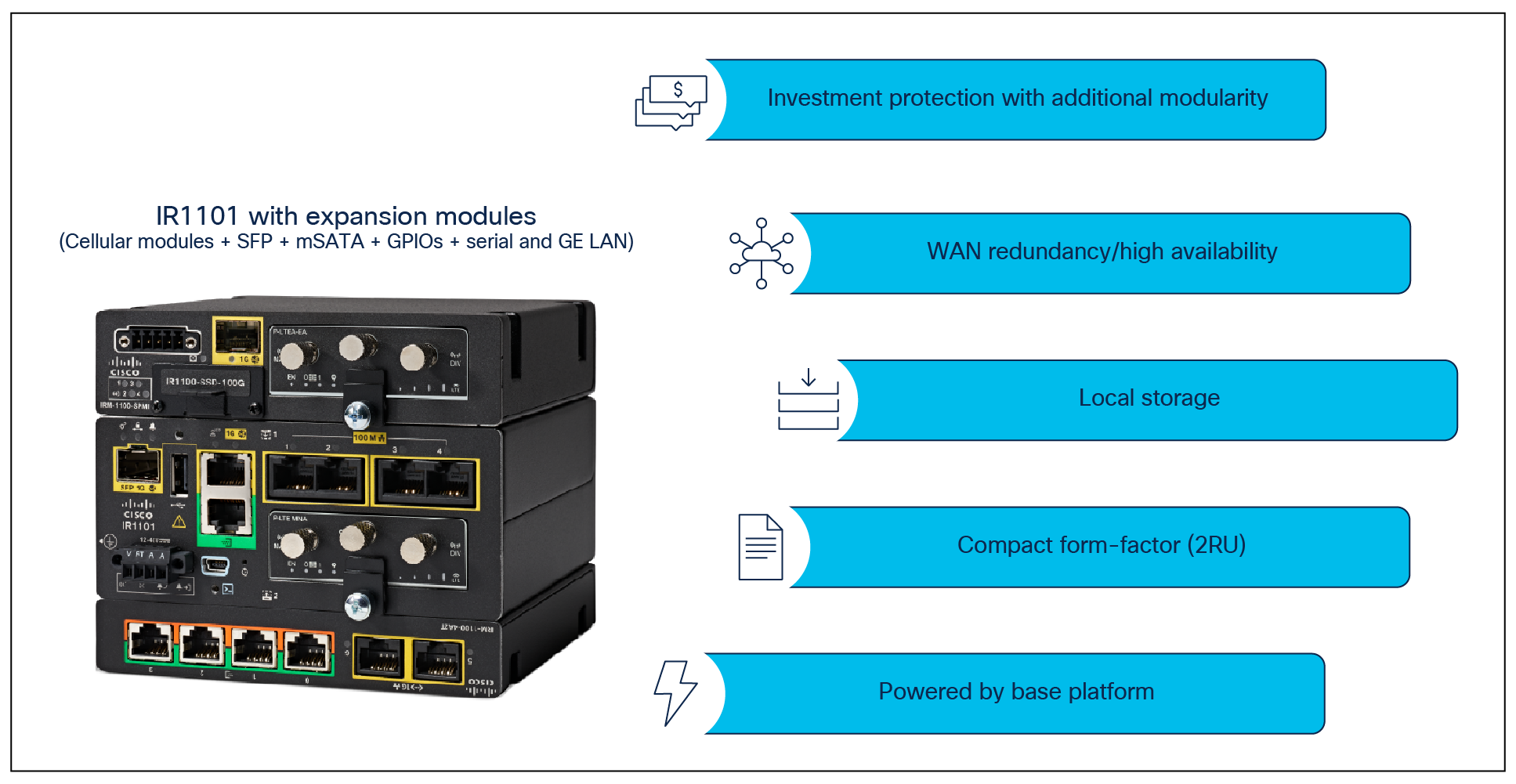
The IR1101 offers even more flexibility to add or upgrade WAN and storage components through an expansion module.
Expansion Modules
IR1101 with expansion module offering more flexibility
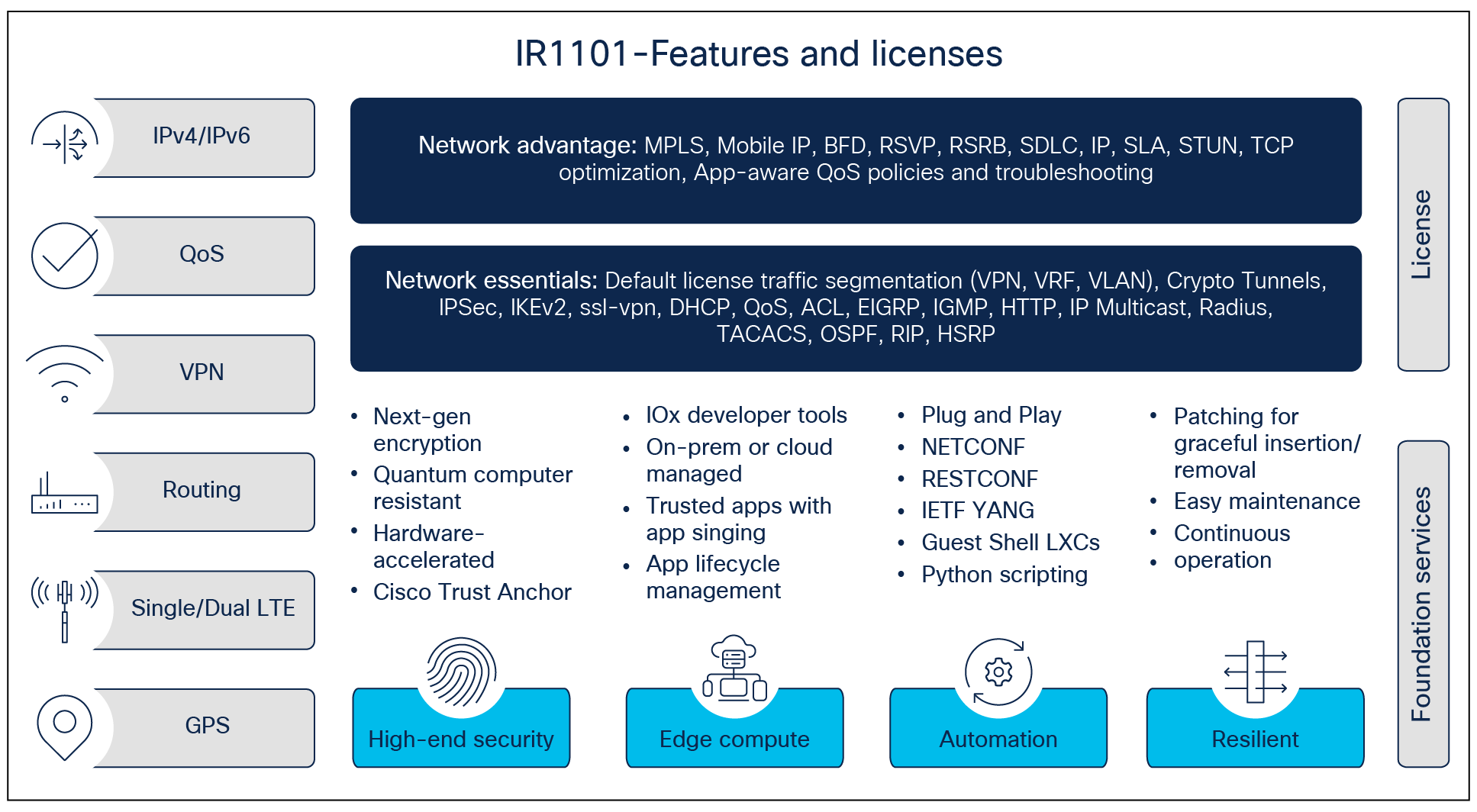
Key features |
|
Modularity and investment protection. A single form factor with multiple WAN (LTE, LTE-Advanced, SFP Ethernet) and storage options enable flexibility to add or upgrade modules as technologies evolve. |
|
|
Dual active LTE-capable With two LTE modules (LTE and LTE-Advanced with carrier aggregation), the IR1101 enables concurrent connectivity to two cellular networks for WAN redundancy, enhanced data throughputs, load balancing, and differentiated services, making it a highly reliable and high-performance platform. |
|
|
Cisco IOS XE Software. IOS XE is a highly secure, standards-based and flexible operating system for a new era of IoT deployment. It’s an enterprise-class OS with advanced routing and security. |
|
|
Software Defined WAN (SDWAN) capable. For high WAN availability and simplicity for large-scale distributed networks. |
|
|
Industrial security. With Cisco Trust Anchor Technology ensuring authenticity of hardware and software, hardware-accelerated Next Generation Encryption and Quantum Computer Resistant algorithms, firewall and VPN services, and alerts and notifications enabling physical and cyber security, the IR1101 offers a multi-layer security for mission-critical deployments. |
|
|
Edge computing. Speed up awareness and response to events and conserve network bandwidth by analyzing the most time-sensitive data at the network edge, close to where it is generated. A highly secure, extensible environment for hosting applications ensures authenticity of applications. An optional mSATA SSD field-replaceable unit on the expansion module enables storage of application data for recording and analysis. |
|
|
Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA). Supports migration of data from legacy control systems in an industrial environment to an IP-based network using DNP3 serial–to–DNP3/IP and IEC 60870 T101–to–T104 protocol translations. |
|
|
Smart grid-compliant. Designed for installation in harsh secondary substation environments. Complies with IEEE 1613 and IEC 61850-3 for distribution automation. |
|
|
GPS. Location-based services for tracking assets and protecting from theft and intrusion. |
|
|
Ease of management. On-premises and cloud-based network management solutions cater to businesses across multiple industry verticals. Tools such as Cisco DNA Center, Cisco IoT Operations Dashboard, Cisco IoT Field Network Director (FND), Cisco Plug and Play (PnP), and Cisco Prime® simplify deployment and offer the breadth of cross-network management and the depth of multi-layer visibility. |
|
|
Multiple Packet Data Network (PDN). Gain connectivity to different Access Point Names (APNs) for traffic segregation over a cellular link. For example, public Internet traffic can be kept separate from mission-critical traffic emerging from the sensors and devices connected to the router. |
|
|
4G LTE multiple-bearer QoS. Differentiated treatment of traffic with multiple simultaneous bearers as per 3GPP standards for an enhanced user experience. Multi-bearer QoS depends on the cellular carrier’s ability to support the service in their network. |
|
|
Network Segmentation. Multi-VRF, VLAN, and VPN enable businesses to configure and maintain more than one instance of a routing and forwarding table within the same customer edge device, enabling dynamic changes in the network with a minimal maintenance window. Service providers can enable this feature to support two or more VPNs with IP addresses that overlap across the VPNs. |
Features |
|
IoT enablement |
||
|
Lightweight, compact, modular, and ruggedized form factor |
Designed for tight installation inside cabinets. All the Input/Output (I/O) ports and connectors are located on the front panel for easy wiring inside cabinets. |
|
|
No additional power supply for the expansion module |
Easily add an expansion module without requiring an additional power input. |
|
|
Raw socket transport and SCADA |
The raw socket can be used to transport SCADA data from RTUs. This method is an alternative to the Block Serial Tunnel (BSTUN) protocol. The Cisco IR1101 also supports DNP3 serial–to–DNP3/IP and IEC 60870 T101–to–IEC 60870 T104 protocol translations, serving as a SCADA gateway. |
|
|
Multiple mounting options |
Floor or wall mounting and DIN rail mounting in horizontal or vertical orientations. |
|
|
Increased performance to run concurrent services |
The multi-core processor architecture allows businesses to take advantage of network-supported speeds. |
|
|
Multiple WAN and LAN connections |
|
|
|
Four fast Ethernet interfaces |
● Allows multiple Ethernet devices (sensors, Remote Terminal Unit [RTU], PLCs) in an industrial environment to connect for visibility and management of assets
● IEEE 802.1Q VLANs
● Layer 3 support through VLAN interfaces
● 4KV isolation for Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) protection
|
|
|
WAN diversity |
● Multiple WAN links for high reliability: Gigabit Ethernet layer 3 SFP (copper and fiber) and 4G LTE provides WAN diversity and business continuity
● Gigabit Ethernet WAN interface can be configured for layer 3 routing or layer 2 switching
|
|
|
Dual active LTE interfaces |
Concurrent connectivity to two cellular networks for high reliability, load balancing, and differentiated services. |
|
|
Serial interface |
A RS-232 asynchronous serial interface (RJ45 DTE) can be used with raw socket, protocol translation, and connections to locate Remote Terminal Unit (RTU), sensors, and PLCs for SCADA transport and management. |
|
|
Transparent roaming between wireless networks |
|
|
|
Dual Subscriber-Identity-Module (SIM) over cellular |
Provides active and backup connectivity for high reliability over LTE and HSPA networks. |
|
|
Cisco IOS® mobile IP |
● Transparent roaming for mobile networks, enabling mission-critical applications to stay connected, even when moving between networks
● The assigned IP addresses to the home network are maintained in private and public networks
● Supports Proxy Mobile IP (PMIPv6) and Network Mobility (NEMO)
|
|
|
Cellular fallback |
Multiple technologies (4G LTE, 3G, and 2G) are available to support connectivity to the best one available. 2G fallback is not supported in North America. |
|
|
Software |
|
|
|
Cisco IOS XE |
Designed to enable businesses to deploy services more quickly with lower TCO and complexity. ● Openness and programmability: Standards-based programmable interfaces enable process and workflow automation. NETCONF, RESTCONF, IETF YANG, Python scripting, and custom libraries enable automation of event-based workflows
● Secure: Multi-level, end-to-end security and trust are built in. The built-in Cisco Next Generation Encryption and Quantum Computing Resistant algorithms are expected to meet security and scalability requirements for the next two decades
● Modular: Enables patching of software bug fixes and graceful insertion and removal of software modules for ease of maintenance
● Common software stack: Reduces business and network complexity while managing an array of Cisco devices
|
|
Network management solutions |
|
Operational phase |
Application |
Description |
|
Device staging and configuration for a few routers |
Cisco WebUI |
A GUI-based device-management tool that simplifies provisioning of devices for a small-scale deployment through easy-to-use wizards. |
|
Deploy, manage, monitor, and maintain IoT gateways and assets at scale |
Cisco IoT Field Network Director (FND) for hosting on premises Cisco IoT Operations Dashboard |
● Rapid scaling — zero-touch deployment and secure enrollment for tens of thousands of gateways
● Enhanced security – role-based access and user audit trail and secure communications for data transport across networks, VPN tunnels, geo-fencing, alerts, and notifications for data and physical security
● Increased reliability – reliable communications over cellular or Ethernet networks, lifecycle management, and 24/7 real-time monitoring and alerts
|
|
Extend your enterprise network to configure, monitor, and manage industrial assets |
Cisco Digital Network Architecture (Cisco DNA1) with APIC-EM Cisco Digital Network Architecture (Cisco DNA) with SDWAN |
● Cisco DNA offers a network infrastructure that is not only fully programmable and open to third–party innovation, but can also fully and seamlessly integrate the cloud as an infrastructure component
● Simplifies and automates processes and workflow by bringing the notion of user-aware and application–aware policies into the foreground of network operations
● With Cisco DNA, the network can provide continuous feedback to simplify and optimize network operations
● Enables automation of network configuration and APIC-EM is a central part of Cisco Digital Network Architecture. It delivers software-defined networking to extend the enterprise network to harsh industrial and outdoor environments
● Single management dashboard for configuration and management of WAN.
● Cisco SD-WAN automates application flexibility over multiple connections, such as the Internet, MPLS, and wireless 4G LTE.
|
|
Manage devices over a cellular network |
Cisco IoT Control Center |
Cisco IoT Control Center minimizes the complexity and cost of managing connected devices on a cellular network by taking control with actionable insights. For instance, tracking and managing data usage overages can result in a significant reduction in operational expenses. |
Embedded management capabilities |
|
Cisco IOS Embedded Event Manager (EEM) |
A distributed and customized approach to event detection and recovery. Provides the ability to monitor events and take corrective or any other desired action when the monitored events, such as a high or low threshold, occur. |
|
Cisco IOS XE IP Service-Level Agreements (IP SLA) |
Helps assure the performance of new, business-critical IP applications as well as IP services by actively monitoring and reliably reporting traffic statistics such as jitter, response time, packet loss, and connectivity. |
|
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), Syslog, NetFlow |
Open-standards-based network monitoring and accounting tools, such as SNMP for 3G, 4G and xDSL MIB, provide a common management platform for many different devices. |
|
LTE network management and diagnostics |
A dedicated diagnostic port on a cellular module enables logging of data during debugging sessions that can be analyzed by industry-standard tools such as Qualcomm CDMA Air Interface Tester (CAIT) and Spirent Universal Diagnostic Monitor (UDM). |
Cisco IOS XE Software Features |
|
Cisco IOS Software requirements |
● Cisco IOS XE Software: Universal Cisco IOS Software image
● Cisco IOS XE Software Release 16.10.1 or later
|
|
IPv4 and IPv6 services features |
● Routing Information Protocol Versions 1 and 2 (RIPv1 and RIPv2)
● Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) and Multipoint GRE (MGRE)
● Standard 802.1d Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
● Network Address Translation (NAT)
● Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server, relay, and client
● Dynamic DNS (DDNS)
● DNS proxy
● DNS spoofing
● Access Control Lists (ACLs)
● IPv4 and IPv6 multicast
● IP Service-Level Agreement (IP SLA)
● Open Shortest Path First (OSPFv2 and OSPFv3)
● Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
● Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP)
● Virtual Route Forwarding (VRF) Lite
● Next-Hop Resolution Protocol (NHRP)
● Serial data encapsulation and relay
● L2TPv3 over sub-interfaces and VLAN
|
|
Security features |
Secure connectivity ● Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) VPN for secure remote access
● Hardware-accelerated encryption with minimal impact to system performance
● Next Generation Encryption (NGE) and Quantum Computing Resistant (QCR) algorithms such as AES-256, SHA-384, and SHA-512
● Public-Key-Infrastructure (PKI) support
● 20 IPsec tunnels
● Cisco Easy VPN Solution client and server
● NAT transparency
● Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN)
● Tunnel-less Group Encrypted Transport VPN
● Flex VPN
● IPsec stateful failover
● VRF-aware IPsec
● IPsec over IPv6
Cisco IOS Firewall ● Zone-based policy firewall
● VRF-aware stateful inspection routing firewall
● Stateful inspection transparent firewall
● Advanced application inspection and control
● Secure HTTP (HTTPS), FTP, and Telnet Authentication Proxy
● Dynamic and static port security
● Firewall stateful failover
● VRF-aware firewall
Integrated Threat Control ● Control-Plane Policing (CoPP)
● Flexible packet matching
● Network foundation protection
|
|
QoS features |
● Provides LTE QoS with support for up to 8 concurrent bearers on each cellular WAN interface for traffic classification and prioritization
● Provides traffic precedence to delay-sensitive and mission-critical services
● Facilitates low-latency routing of delay-sensitive industrial applications
● Supported on all LAN and WAN interfaces, including cellular
● Low Latency Queuing (LLQ)
● Weighted Fair Queuing (WFQ)
● Class-Based WFQ (CBWFQ)
● Class-Based Traffic Shaping (CBTS)
● Class-Based Traffic Policing (CBTP)
● Policy-Based Routing (PBR)
● Class-Based QoS MIB
● Class of Service (CoS) to Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) mapping
● Class-Based Weighted Random Early Detection (CBWRED)
● Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP)
● Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP) header compression (cRTP)
● Differentiated Services (DiffServ)
● QoS pre-classify and pre-fragmentation
● Hierarchical QoS (HQoS)
|
|
High-availability features |
● Dual active LTE backhaul with expansion module
● Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) (RFC 2338)
● Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP)
● Dual SIM support on the LTE module for cellular failover
|
|
IPv6 features |
● IPv6 addressing architecture
● IPv6 unicast and multicast forwarding
● IPv6 ACLs
● IPv6 over cellular
● IPv6 routing
● IPv6 domain name resolution
|
Software licensing |
Specifications |
|
Memory |
|
|
Default and maximum DRAM |
4 GB |
|
Default and maximum Flash memory |
8 GB (physical) / 4 GB (usable) |
|
Ingress protection rating |
IP30 |
|
Physical characteristics |
|
|
Physical dimensions (H x W x D) Chassis Expansion Module |
2.36 in. x 5.22 in. x 4.92 in. (60 x 132.5 x 124.9 mm) 1.3 in. x 5.2 in. x 4.9 in. (33 x 132 x 124 mm) |
|
Weight Chassis Expansion Module IRM-1100-SPMI: IRM-1100-SP: |
2.25 lbs (1.02 kg) 1.65 lbs (0.75 kg) 1.45 lbs (0.66 kg) |
|
Mounting options |
Panel, wall, and din rail (vertical and horizontal) mount |
|
Nominal voltage: /-12V to /-48V DC Minimum and maximum input voltage: 9.6-60V DC Maximum and minimum input current: 1.24A (9.6V DC) and 0.26A (60V DC) |
|
|
Power consumption |
At idle: 6.6W Typical: 9.8W Maximum: 12W Additional 10W (typical) with expansion module and 2nd cellular |
|
Interfaces on the base platform |
|
|
Console |
Mini type-B USB |
|
WAN interfaces |
● Combo 10/100/1000 Gigabit Ethernet port (RJ45 and SFP) on the base platform
● An additional 10/100/1000 Gigabit Ethernet SFP on the expansion module. Refer to Table 8 for supported SFPs
● LTE: Modular with options for single and dual active LTE and LTE-Advanced
|
|
LAN interfaces |
● Four 10/100BASE-T Fast Ethernet ports
|
|
Input and output |
● ALARM input port
|
|
LEDs |
● System OK
● Link for Ethernet WAN ports
● VPN
● Tricolor user-configurable LED
● ALARM
|
|
Serial interface |
● Isolated RS-232 RJ45 DTE port
● Support for asynchronous mode with speeds up to 115,200 baud
|
|
Serial protocols |
SCADA, DNP3, T101-104, Raw Socket TCP, and UDP |
|
Environmental characteristics |
|
|
Environmental operating temperature range |
–40 to 140°F (–40 to 60°C) in a sealed NEMA cabinet with no airflow –40 to 158°F (–40 to 70°C) in a vented cabinet with 40 Linear Feet per Minute (LFM) of air –40 to 167°F (–40 to 75°C) in a forced air enclosure with 200 LFM of air Type tested at 85°C for 16 hours |
|
Operating altitude |
40°C up to 13,800 ft (operating) per IEC 68-2-41 |
|
Non-operating shock and vibration |
● 50-60G (3.76 m/s minimum)
● 3-500Hz at 1.12 GRMS (BP at 10 and 100 Hz)
|
|
Standard safety certifications |
● UL 60950-1, 2 nd edition
● CAN/CSA C22.2 No. 60950-1, 2 nd edition
● EN 60950-1, 2 nd edition
● CB to IEC 60950-1, 2 nd edition with all group differences and national deviations
|
|
Hazardous locations standards |
● ANSI/ISA 12.12.01 (Class 1, Div 2 A-D)
● CSA 213 (Class 1, Div 2 A-D)
● IEC 60079-0 and -15 IECEx test report (Class I, Zone 2, gas groups IIC)
● EN 60079-0 and -15 ATEX certification (Class I, Zone 2, gas groups IIC)
|
|
Industry standards |
Public Safety: ● FirstNet Ready ™
Smart Grid: ● IEC 61850-3
● IEEE 1613
Security: ● FIPS 140-2
● Common Criteria
Department of Defense ● DoDIN APL
IPv6 ● USGv6
|
|
EMC emissions CLASS A |
● 47 CFR Part 15 B
● EN 55032:2015
● CISPR 32 Edition 2
● CNS13438: 2006
● EN 300 386 V1.6.1
● ICES-003 Issue 6: 2016
● KN 32: 2015
● TCVN 7189: 2009
● V-2/2015.04
● V-3/2015.04
● AS/NZ CISPR32
|
|
EMC immunity |
● EN 61000-4-2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 16, 17, 18, and 29
● CISPR24: 2010 A1: 2015
● EN 300 386 V1.6.1
● EN 55024: 2010 A1: 2015
● EN 55035:2017
● KN35: 2015
● TCVN 7317:2003
● QCVN 18:2014
|
LTE (3GPP Category 4) modules available with the IR1101 |
|
Region theaters |
P-LTE-MNA |
P-LTE-VZ |
P-LTE-US |
P-LTE-GB |
|
LTE bands |
LTE bands 2,4,5,12,13,14,17,66 FDD LTE 1700 MHz and 2100 Mhz (band 66 Ext AWS), 700 Mhz (band 17, 14, 13,12), 850 Mhz (band 5 CLR), 1700 MHz and 2100 MHz (band 4 AWS), 1900 Mhz (band 2) |
LTE bands 4, 13 FDD LTE 700 MHz (band 13), 1700 MHz and 2100 MHz (band 4 AWS) |
LTE bands 2, 4, 5, 12 FDD LTE 700 MHz (band 17), 700 MHz (band 12), 850 MHz (band 5 CLR), 1700 MHz and 2100 MHz (band 4 AWS) |
LTE bands 1, 3, 7, 8, 20, 28 FDD LTE 700 MHz (band 28), 800 MHz (band 20), 900 MHz (band 8), 1800 MHz (band 3), 2100 MHz (band 1), and 2600 MHz (band 7) |
|
Backward compatibility |
UMTS, HSPA (band 2,4,5) |
— |
HSPA (band 2, 4, 5) |
UMTS, HSPA (band 1, 8), EDGE, GSM, GPRS (900/1800) |
|
Theoretical download and upload speeds1 |
150 and 50 Mbps |
150 and 50 Mbps |
150 and 50 Mbps |
150 and 50 Mbps |
|
United States |
Multicarrier (AT&T and Verizon) |
Verizon |
AT&T |
— |
|
Europe |
— |
— |
— |
Yes |
|
Band 14 |
Yes |
— |
— |
— |
|
FirstNet Ready™ |
Approved by AT&T FirstNet |
— |
— |
— |
|
Region theaters |
P-LTE-IN |
P-LTE-JN |
|
LTE bands |
LTE bands 1, 3, 5, 8, 40, 41* FDD LTE 2100 MHz (band 1), 1800MHz (band 3), 850MHz (band 5) , 900MHz (band 8) TDD LTE 2300 MHz (band 40), 2500MHz (band 41). *B41 supported frequency range: (2535–2655 MHz) |
LTE bands 1, 3, 8, 11, 18, 19, 21 FDD LTE 2100 MHz (band 1), 1800MHz (band 3), 900Mhz (band 8), 1500MHz (band 11), 850MHz (band 18 and band 19), 1500MHz (band 21) |
|
Backward compatibility |
HSPA , UMTS (band 1, 8) |
HSPA , UMTS (band 1, 6, 19) |
|
Theoretical download and upload speeds3 |
150 and 50 Mbps |
150 and 50 Mbps |
|
India |
Yes |
— |
|
Japan |
— |
Yes (NTT Docomo, KDDI, Softbank) |
LTE Advanced (3GPP Category 6) modules available with the IR1101 |
|
Region theaters |
P-LTEA-EA |
P-LTEA-LA |
|
LTE bands |
LTE bands 1-5, 7, 8, 12, 13, 20, 25, 26, 29, 30, and 41 FDD LTE 700 MHz (band 12), 700 MHz (band 29), 800 MHz (band 20), 850 MHz (band 5 CLR), 850 MHz (band 26 Low), 900 MHz (band 8), 1800 MHz (band 3), 1900 MHz (band 2), 1900 MHz (PCS band 25), 1700 MHz and 2100 MHz (band 4 AWS), 2100 MHz (band 1), 2300 MHz (band 30), or 2600 MHz (band 7) TDD LTE 2500 MHz (band 41) Carrier aggregation band combinations: 1 8; 2 (2,5,12,13,29); 3 (7,20); 4 (4,5,12,13,29); 7 (7,20); 12 30, 5 30, and 41 41 |
LTE bands 1, 3, 5, 7, 8, 18, 19, 21, 28, 38, 39, 40, and 41 FDD LTE 700 MHz (band 28), 850 MHz (band 5 CLR), 850 MHz (bands 18 and 19 Low), 900 MHz (band 8), 1500 MHz (band 21), 1800 MHz (band 3), 2100 MHz (band 1), or 2600 MHz (band 7) TDD LTE 1900 MHz (band 39), 2300 MHz (band 40), 2500 MHz (band 41), or 2600 MHz (band 38) Carrier aggregation band combinations: 1 (8,18,19,21); 3 (5,7,19,28); 7 (5,7,28); 19 21, 38 38, 39 39,40 40, and 41 41 |
|
Theoretical download and upload speeds3 |
300 and 50 Mbps |
300 and 50 Mbps |
|
United States |
Verizon, AT&T |
— |
|
Europe |
— |
— |
|
Canada |
Yes |
|
|
Australia and New Zealand |
— |
Yes (Approved by Telstra) |
|
Japan |
— |
Yes (NTT Docomo, KDDI, Softbank) |
|
India, Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand |
|
Yes |
|
United Arab Emirates |
Yes |
|
LTE Advanced Pro (3GPP Category 18) module available with the IR1101 |
|
Region theaters |
P-LTEAP18-GL1 |
|
LTE bands |
LTE bands 1-5, 7, 8, 12-14, 17, 18-20, 25, 26, 28-30, 32, 38-43, 46, 48, 66, and 71. FDD LTE 600 MHz (band 71), 700 MHz (bands 12, 13, 14, 17, 28, and 29), 800 MHz (band 20), 850 MHz (bands 5, 18, 19, and 26), 900 MHz (band 8), 1500 MHz (band 32), 1700 MHz (bands 4 and 66), 1800 MHz (band 3), 1900 MHz (bands 2 and 25), 2100 MHz (band 1), 2300 MHz (band 30), 2600 MHz (band 7). TDD LTE 1900 MHz (band 39), 2300 MHz (band 40), 2500 MHz (band 41), 2600 MHz (band 38), 3500 MHz (bands 42 and 48), 3700 MHz (band 43), 5200 MHz (band 46). |
|
Theoretical download and upload speeds2 |
1.2 Gbps/200 Mbps |
|
United States |
Multicarrier (AT&T and Verizon) |
|
Europe |
Yes |
|
Canada |
Yes (Bell) |
|
Australia |
Yes |
|
Japan |
Yes |
|
Band 14 |
Yes |
|
FirstNet Certification |
Completed |
|
Band 48 (CBRS) |
Yes |
xDSL module |
|
xDSL SFP |
Transmission Modes |
Classification |
Countries/Region supported2 |
|
SFP-VADSL2 -I |
VDSL2, ADSL2/2 |
Industrial (-20C to 60C) |
UK, Europe, Australia |
|
VDSL2 Transmission Mode |
|
|
|
|
Band Plan |
ITU-T G.933.2 with 6 band (30MHz) US0 band support |
Frequency Plan |
Annex A (998) Annex B (997, 998) |
|
Profile |
8a, 8b, 8c, 8d, 12a, 12b, 17a |
OLR |
Bit Swapping, SRA, SOS, Dynamic Interleaver Depth (D) change |
|
Theoritical Data Rate |
DS/US: 200Mbps/100Mbps |
Diagnostic |
DELT |
|
ADSL2/2 Transmission Mode |
||
|
Annex |
A/L |
|
|
Theoritical Data Rate |
DS/US: 24Mbps/1Mbps |
|
|
Modes |
PTM Mode (CPE) |
|
|
Hardware |
RJ-45 female connector |
|
|
SERDES connect to host |
|
|
|
DSL specific IOS XE features |
VPI/VCI management, Firmware upgrade, PPPoE |
|
|
Power Requirement |
3.3V, 700mA |
|
|
Operating Temperature |
-40C to 60C |
|
|
Operating Humidity |
10% to 90% (non-condensed) |
|
|
Surge Protection |
Compliant with ITU-T K.21 Enhanced Mode (Differential Mode: 1.5KV, Common Mode: 6KV |
|
|
Certification |
RoHS/CE/FCC/CB |
|
Supported Ethernet SFP modules |
|
GE SFP |
Distance |
Fiber |
Classification |
|
GLC-SX-MM-RGD |
220-550 m |
MMF |
Industrial (-40C to 85C) |
|
GLC-LX-SM-RGD |
550m / 10 km |
MMF / SMF |
Industrial (-40C to 85C) |
|
GLC-ZX-SM-RGD |
70 km |
SMF |
Industrial (-40C to 85C) |
|
GLC-SX-MMD |
220-550m |
MMF |
Extended (-5C to 85C) |
|
GLC-LH-SMD |
550m / 10 km |
MMF/SMF |
Extended (-5C to 85C) |
|
GLC-ZX-SMD |
70 km |
SMF |
Extended (-5C to 85C) |
|
GLC-BX-U |
10 km |
SMF |
Commercial (0C to 70C) |
|
GLC-BX-D |
10 km |
SMF |
Commercial (0C to 70C) |
|
GLC-LH-MMD |
550m / 10km |
MMF/SMF |
Extended (-5C to 85C) |
|
GLC-EX-SMD |
40 km |
SMF |
Extended (-5C to 85C) |
|
GLC-FE-100FX-RGD |
2 km |
MMF |
Industrial (-40C to 85C) |
|
GLC-FE-100LX-RGD |
10 km |
SMF |
Industrial (-40C to 85C) |
|
GLC-FE-100FX |
2 km |
MMF |
Commercial (0C to 70C) |
|
GLC-FE-100LX |
10 km |
SMF |
Commercial (0C to 70C) |
|
GLC-FE-100EX |
40 km |
SMF |
Commercial (0C to 70C) |
|
GLC-FE-100ZX |
80 km |
SMF |
Commercial (0C to 70C) |
|
GLC-FE-100BX-U |
10 km |
SMF |
Commercial (0C to 70C) |
|
GLC-FE-100BX-D |
10 km |
SMF |
Commercial (0C to 70C) |
|
GLC-TE |
100m |
NA (RJ45) |
Extended (-5C to 85C) |
Note: The IR1101 is designed to operate in the industrial temperature range (-40C to 85C internal component temperature range) and therefore, using a non-industrial or commercial-rated SFP modules could bring down the temperature profile of the system.